-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 26
1. Security Architecture
스프링 시큐리티가 추구하는 보안 아키텍처를 이해하면 스프링 시큐리티에 다가가는 것이 조금 더 쉬워집니다.
스프링 시큐리티는 기본적으로 인증(Authentication)과 권한 부여(Authorization)이라는 두 가지 영역을 기반으로 보안을 적용합니다. 그래서 이 두 가지 영역에 대해서 이해하는 것이 가장 중요합니다.
첫번째로 알아볼 영역은 인증(Authentication)입니다. 인증은 애플리케이션 사용자가 애플리케이션에게 자신의 신원을 제공하는 과정입니다. 예를 들어, 일반적인 인증 시나리오를 고려해본다면 구글이나 네이버같은 웹사이트를 이용하기 위하여 계정과 비밀번호와 같은 신원을 파악할 수 있는 정보를 제공하고 웹사이트는 제공된 신원 정보를 통해 신뢰할 수 있는 사람인가를 파악하게 됩니다. 최종적으로 웹 사이트는 인증된 사용자라고 저장합니다.
스프링 시큐리티는 인증 영역에서 인증 처리 프로세스를 담당하는 주요 인터페이스인 AuthenticationManager로써 담당합니다.
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}AuthenticationManager는 authenticate라는 함수로 Authentcation 요청 정보를 받아 인증된 Authentcation을 제공합니다.
가장 일반적으로 사용되는 AuthenticationManager 구현체는 ProviderManager로 AuthenticationProvider 인스턴스 체인에 인증을 위임하게 됩니다.
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}즉, 여러가지 AuthenticationProvider가 담당하는 Authentication 유형에 따라 인증을 처리하게 됩니다. 이 말은 하나의 Provider가 대부분의 Authentication에 대한 인증을 담당할 수도 있고 개별적으로 분리시켜 인증을 담당하게 할 수 있다는 말이 됩니다.

Figure 1. An AuthenticationManager hierarchy using ProviderManager
AuthenticationManager가 인증을 처리하는 것까지는 알게되었습니다. 그러면 인증된 Authentication을 저장하고 가져오는 것은 어떻게 하는 것일까요? 바로 SecurityContextHolder가 이 부분을 담당하게 됩니다. SecurityContextHolder는 인증 과정에서 AuthenticationManager에 의해 인증된 Authentication을 저장하고 원래 요청을 처리할 수 있도록 넘겨줍니다.
예를 들어, 일반적인 웹 애플리케이션인 경우에 HTTP 요청 사이에 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter가 SecurityContext에 Authentication을 저장하는 것을 담당하게 됩니다.
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter가 어느 위치에서 동작하는지 알고 싶다면 FilterChain 페이지를 참고하세요
SecurityContextHolder는 애플리케이션 내에서 현재 보안 컨텍스트(Security Context)에 인증 정보를 저장합니다. 그리고 SecurityContextHolder는 기본적으로 ThreadLocal로써 동작하므로 하나의 요청에 대하여 같은 컨텍스트 내에서 동작한다면 어느 곳에든지 SecurityContextHolder를 통해 인증된 Authentcation 정보를 가져올 수 있습니다.
public void doSomething() {
SecurityContext securityContext = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication authentication = securityContext.getAuthentication();
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
}SecurityContextHolder를 통해 현재 스레드의 SecurityContext를 가져올 수 있으며 SecurityContext를 통해 저장된 Authentcation 정보를 가져올 수 있습니다. 그리고 Authentication이 인증되었다면 인증된 주체(Principal) 정보도 가져올 수 있습니다.
여기서 인증된 주체(Principal)은 사용자 정보라고 이해하시면 됩니다.
보통 단순 사용자 이름이거나UserDetails와 같은 사용자 정보를 가지는 클래스입니다.
우리는 인증 영역을 통해 AuthenticationManager가 인증을 담당하여 SecurityContextHolder가 인증 정보를 SecurityContext에 저장하게 된다는 걸 알게 되었습니다!
두번째는 권한 부여(Authorization)라는 영역입니다. 이 영역은 접근 제어(Access Control)이라는 보안 전략과 연관되어 있습니다.
사실 Authentication 인터페이스는 부여된 권한이라는 GrantedAuthority 목록을 가지고 있습니다. 이는 인증 주체에게 부여된 권한을 의미합니다. 그리고 요청을 처리하는 과정에서 AccessDecisionManager가 부여된 권한 목록을 확인하여 접근할 수 있는지를 제어합니다.
AccessDecisionManager는 AbstractSecurityInterceptor에 의해 호출되고 최종 접근 제어를 결정합니다.
AccessDecisionManager 인터페이스가 포함하는 메소드를 살펴보겠습니다.
void decide(Authentication authentication, Object secureObject,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attrs) throws AccessDeniedException;
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class clazz);supports(ConfigAttribute attribute)는 AbstractSecurityInterceptor에 의해 호출되어 AccessDecisionManager가 접근 제어를 결정할 지 선택하게 됩니다. 그러면 AccessDecisionManager가 접근 제어를 어떻게 결정하는 것일까요?
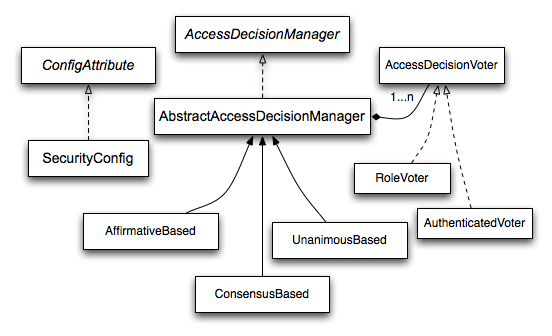
다음 그림을 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
***Based, ***Voter 와 AccessDecisionVoter가 보입니다.
AuthentcationProvider가 최종 접근 제어를 결정할 AccessDecisionManager를 선택하는 것을 AccessDecisionVoter 체인에 위임합니다.
public interface AccessDecisionVoter<S> {
int ACCESS_GRANTED = 1;
int ACCESS_ABSTAIN = 0;
int ACCESS_DENIED = -1;
boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute);
boolean supports(Class<?> clazz);
int vote(Authentication authentication, S object,
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes);
}RoleVoter는 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 유권자입니다. 이는 인증 주체가 가진 롤 이름에 따라 접근 권한을 부여하기 위해 투표합니다.
AuthenticatedVoter는 익명, 완전 인증 그리고 리멤버-미 인증 사용자를 구별하는데 사용됩니다.
AccessDecisionManager는 AccessDecisionVoter들의 투표에 따라 접근 제어를 최종적으로 결정하게 됩니다.
투표에 따라 접근 제어를 결정한다는 의미는 유권자가 접근을 거부한다해도 이를 무시할 수 있다는 말입니다.
만약, AccessDecisionManager가 접근을 거부하게되면 AccessDeniedException 예외가 발생하게 됩니다.
이로써 우리는 스프링 시큐리티의 두가지 보안 영역, 인증 그리고 권한 부여에 대해서 알아보았습니다.
이제 이해한 것을 토대로 스프링 시큐리티를 적용하시면 됩니다.