A Velocity obstacle (VO) refers to the set of all velocities of a robot which will result in collision with another robot moving in the same space. This formulation is used in obstacle avoidance such that we make sure that the robot(s) choose(s) a velocity which does not lie in VO thereby, avoiding collision. There are two methods to solve this problem
- (a) By framing it as a sampling problem
- (b) By framing it as an optimization problem
At each time step, we look at all the possible velocities which the robot may take, subject to the constraint that the chosen velocity lies between a user-specified range of minimum and maximum velocities (v_min and v_max respectively). Then, from among these velocities we look at all the velocities which do not lead to a collision. And then from among the set of velocities which lie between v_min and v_max and also don’t lead to a collision, we choose the velocity which minimizes the distance between robots present position and its goal. Note: For the purpose of this assignment, we have framed the problem as a sampling problem, and have solved it for the case of a holonomic robot.
| 1 Main agent + 3 obstacles | 1 Main agent + 3 obstacles | 1 Main agent + 2 obstacles |
|---|---|---|
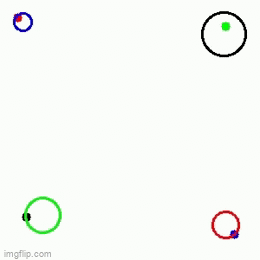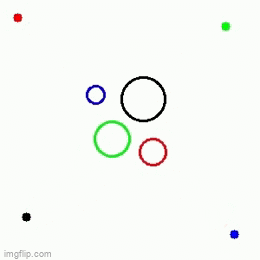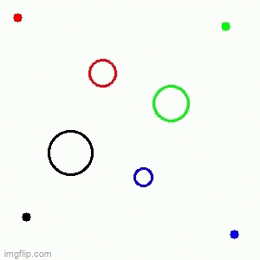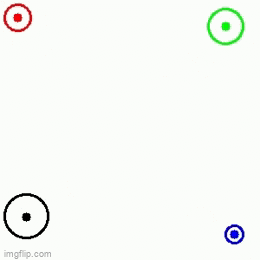 |
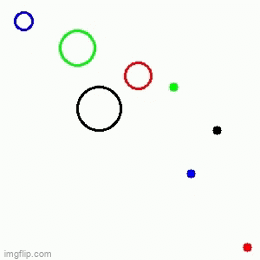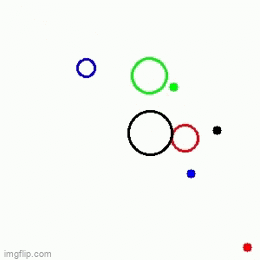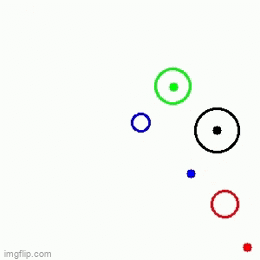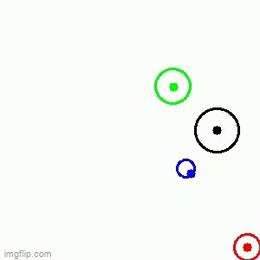 |
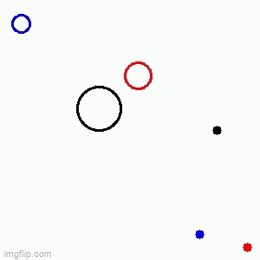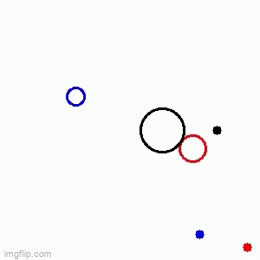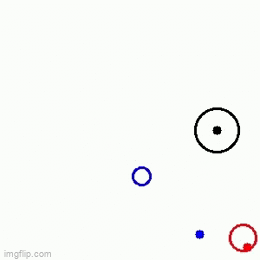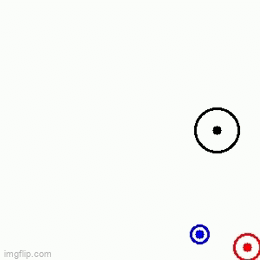 |
- Create an empty image. This empty image represents our world.
- Create a set of robots. (Note: In order to ease the coding process, the dynamic obstacles too have been modelled as robots and our “main” robot tries to avoid collision with these moving robots)
- Define the parameters to those robots. This is done by calling the addRobot() function
- Once the robot parameters have been added, they are added to our world by calling the createWorld() function
- Once all the parameters have been created, we go to the solver() function. The solver() function is the main function which solves the problem
- Inside the solver function, we do the following:
- 6.1 For all robots
-
- 6.1.1 Get a set of velocities which lie in range v_min and v_max
-
- 6.1.2 Now, from among these set of velocities, further filter to get the set of velocities which do not result in a collision.
-
- 6.1.3 Once the set of velocities which do not result in a collision have been identified, from these velocities, choose the velocity which minimizes the distance between robots present location and its goal.
- 6.2 Keep doing the above process for each robot, till the robot is within a threshold distance of its goal.
- 6.3 In case the number of iterations go beyond a threshold maximum number of iterations, then exit even if the goal is not reached. This is done to prevent the program from going into an infinite loop for the cases where a solution is not possible.
srcfolder contains the source code.resultsfolder contains the outputs obtained for different number of obstacles and different start and goal points
Any changes which need to be made, must be made in the code block under the heading "Main" only
- Open your software of choice (Google Colab, Jupyter Notebook etc.)
- Navigate to
srcfolder. (If using Google Colab, upload the file insidesrcfrom your local PC to the colab repository) - Load the file
- Run the file
- If you want to make any changes to things like number of robots, goal point of robots, where to save the outputs, whether you want to save outputs or not etc., make necessary changes in the cell block under the heading "Main". The cell block is self-explanatory.
- Install any necessary libraries if needed
- In the cell block under the heading "Main", make changes to the line where
solverfunction is called. Instructions regarding how the changes required can be understood by reading the function documentation. - Note: Please make sure that an empty directory exists at the path given to the program to save outputs